Engineering Design Process: How we solve problems
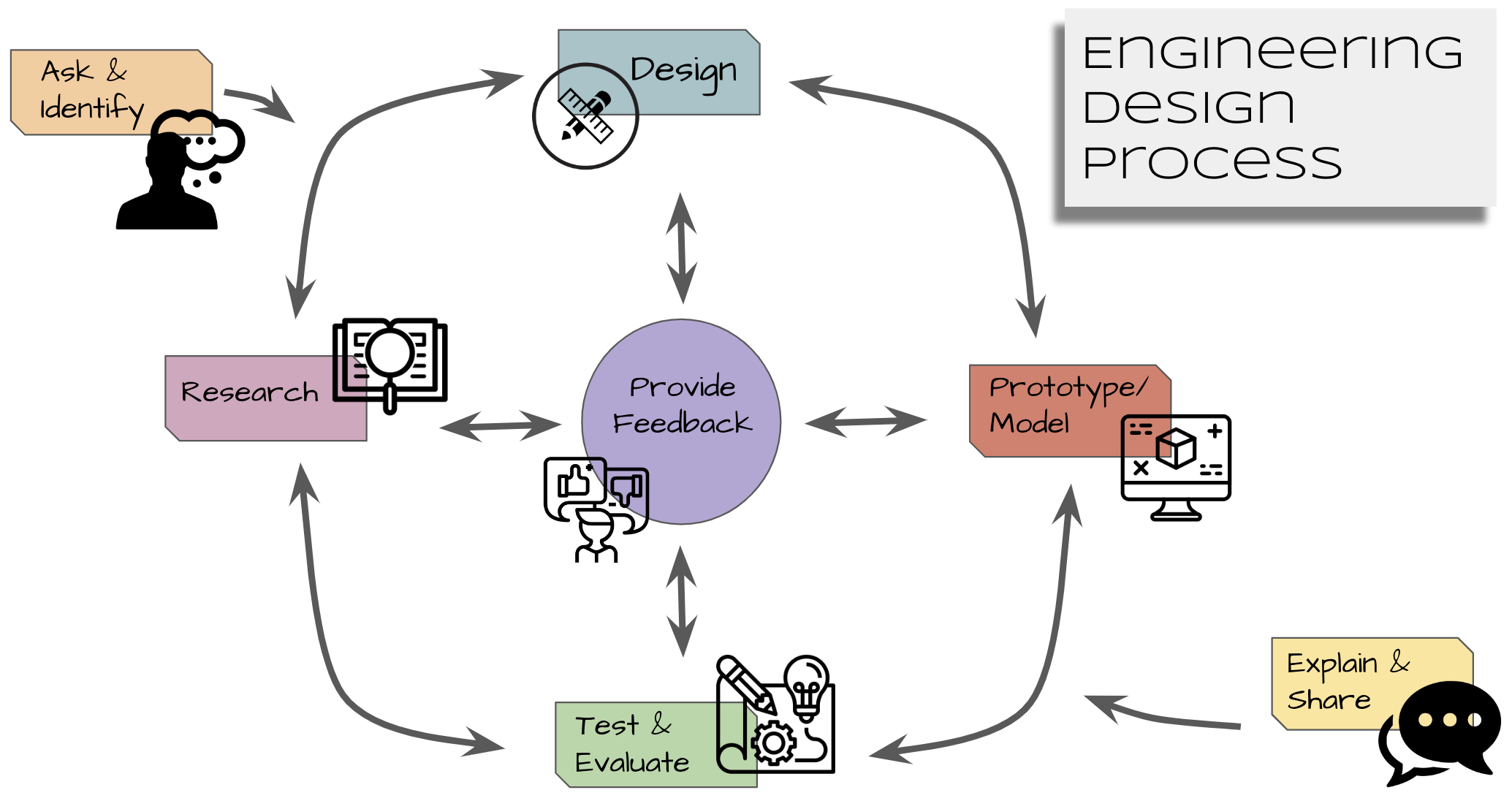
The Engineering Design Process
The Engineering Design Process is a series of steps that engineers follow to come up with a solution to a problem. When we say “problem”, we mean either a task given that needs to be completed or a solution to a problem or issue that needs to be solved.
This might mean creating a prototype (the first design or preliminary model of something, especially a machine, from which other forms are developed or copied) that meets certain criteria given by a supervisor or people who are in need of the solution. Usually the Engineering Design Process is a step by step diagram or procedure - where there is a set beginning and a set ending. Engineers do not always follow the engineering design process steps in order, one after another
It is very common to design something, test it, find a problem, and then go back to an earlier step to make a modification or change to your design. This way of working is called iteration (meaning a repetitive process) and it is likely that your process will do the same! The diagram above is my personal interpretation of the Engineering Design Process (or EDP for short) and is how I see engineers work when trying to solve problems. As you can see, there is no beginning or end clearly labeled. Sometimes during research, one might find a problem that they want to solve. Or maybe during the test and evaluate, an engineer comes up with a new problem that might inspire a new type of prototype unrelated to what they are doing. Providing feedback is central to this process (hence it being in the center) and happens at all times!
Models and Prototypes
The main difference between a model and a prototype is their purpose and functionality: A Model focuses on the visual and aesthetic aspects of an invention, such as its design, form, and appearance. Models are used to represent concepts, and can help with analysis, communication, and definition.
A Prototype focuses on the practicality and functionality of an invention, such as how it works and its technical aspects. Prototypes are used to test the design or building process, and are usually created in the early stages of development.
Prototypes are often used to test if a final piece will work as intended, such as its size, geometry, or function. Issues found and resolved during the prototyping stage can save on production and tooling costs.
So a simple way to summarize this is that a model is a visual representation that doesn't function, but a prototype is a visual representation that has function to it. You can check out this video to learn more about how to use the EDP to solve problems: Video Tutorial!
Quick Summary
Engineering Design Process
The Engineering Design Process is a series of steps that engineers follow to come up with a solution to a problem. Through multiple iterations, talking with members of your group, and researching how other people do things, we can use this to help us solve all kinds of problems.
Prototypes
A Prototype focuses on the practicality and functionality of an invention, such as how it works and its technical aspects. Prototypes are used to test the design or building process, and are usually created in the early stages of development.
Models
A Model focuses on the visual and aesthetic aspects of an invention, such as its design, form, and appearance. Models are used to represent concepts, and can help with analysis, communication, and definition.